Cross System Optimization (CSO)
Cross System Optimization (CSO) is an variation of the generic CSS concept.
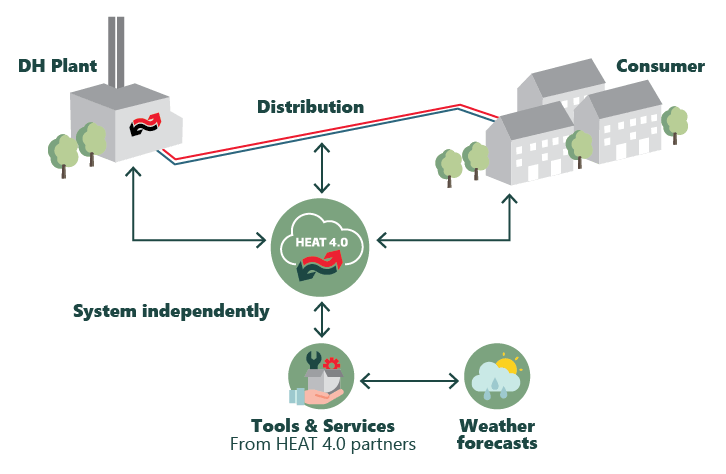
The target is to optimize the district heating system across the whole system. There can be different targets for such optimizations in general, but similar for the CSO solution. One possible objective can be the optimization of the supply temperature that determines the heat losses in the net (to be minimized), the sum of energy used for the production, the amount of heat delivered or many other targets.
Please note that concept ‘cross system’ can be done across different dimensions, e.g. a component or a termporal dimension. The work presented here is describing a single implementation – a service that optimizes across the three main components, including Production (PO), distribution in the district heating Network (NO) and demand from typical Buildings (BO) .
The CSO concept can be implemented in various ways, involving a various number of components and different combinations of these that we will call configurations.
There are basically two main configurations addressed in current solutions:
1. Peer to Peer (p2p)
2. Peer to Cloud to Peer (p2c2p)
The former implements (standardized) communication between each involved software package, whereas the latter employs communication in a star-constellation, where every software package is talking to the ‘common cloud’ component and this common component dispatches the communication to the other parties involved in a given solution.
The ‘Cloud’ is a data-sharing component. In future solutions, additional ‘common component’ can be imagined, hence the ‘c’ can stand for ‘Common Components’ and the configuration can be called ‘Peer to Common Component to Peer’.
HEAT 4.0, has produced a number of reports that are collected on this page: Final reporting. You will find a detailed description and evaluation of the Cross System Optimization solutions there. This page represents the final report to the funding body, the Innovation Fund Denmark. Thanks to the foundation for this financial support.
Cross System Optimization (CSO)
Cross System Optimization (CSO) is an variation of the generic CSS concept. The target is to optimize the district heating system across the whole system.
There can be different targets for such optimizations in general, but similar for the CSO solution. One possible objective can be the optimization of the supply temperature that determines the heat losses in the net (to be minimized), the sum of energy used for the production, the amount of heat delivered or many other targets.
Please note that this could be done across different dimensions, but the work presented here is describing a single implementation – a service that optimizes across the three main components, including Production (PO), distribution in the district heating Network (NO) and demand from typical Buildings (BO) .
The CSO concept can be implemented in various ways, involving a various number of components and different combinations of these that we will call configurations.
There are basically two main configurations addressed in current solutions:
1. Peer to Peer (p2p)
2. Peer to Cloud to Peer (p2c2p)
The former implements (standardized) communication between each involved software package, whereas the latter employs communication in a star-constellation, where every software package is talking to the ‘common cloud’ component and this common component dispatches the communication to the other parties involved in a given solution.
The ‘Cloud’ is a data-sharing component. In future solutions, additional ‘common component’ can be imagined, hence the ‘c’ can stand for ‘Common Components’ and the configuration can be called ‘Peer to Common Component to Peer’.
HEAT 4.0, has produced a number of reports that are collected on this page: Final reporting. You will find a detailed description and evaluation of the Cross System Optimization solutions there. This page represents the final report to the funding body, the Innovation Fund Denmark. Thanks to the foundation for this financial support.